
Exemplary seize of the proposed power-saving methodology
Gosala Kulupana (BBC R&D)
Excessive dynamic vary (HDR) know-how offers a wide range of luminance values and consequently elevates the perceived high quality in video content material. On the similar time, HDR content material consumes a considerable amount of energy when displayed on appropriate units. We now have analysed the facility consumption of the show throughout completely different HDR content material and some completely different HDR TV units and proposed Simply Noticeable Distinction (JND) based mostly algorithms to scale back the facility consumption with a minimal impression on the person notion.
The circulation chart beneath illustrates the structure of the proposed algorithms. An autoregression mannequin is first employed for every pixel to calculate two parts: orderly parts (those which might be predictable from the encompassing), and disorderly parts (those that aren’t predictable from the encompassing). The orderly parts usually correspond to low-frequency components of the picture and therefore are extra delicate to human eyes than the disorderly parts. They’re later used as inputs to compute a number of visible masks which might be later utilized on video frames.
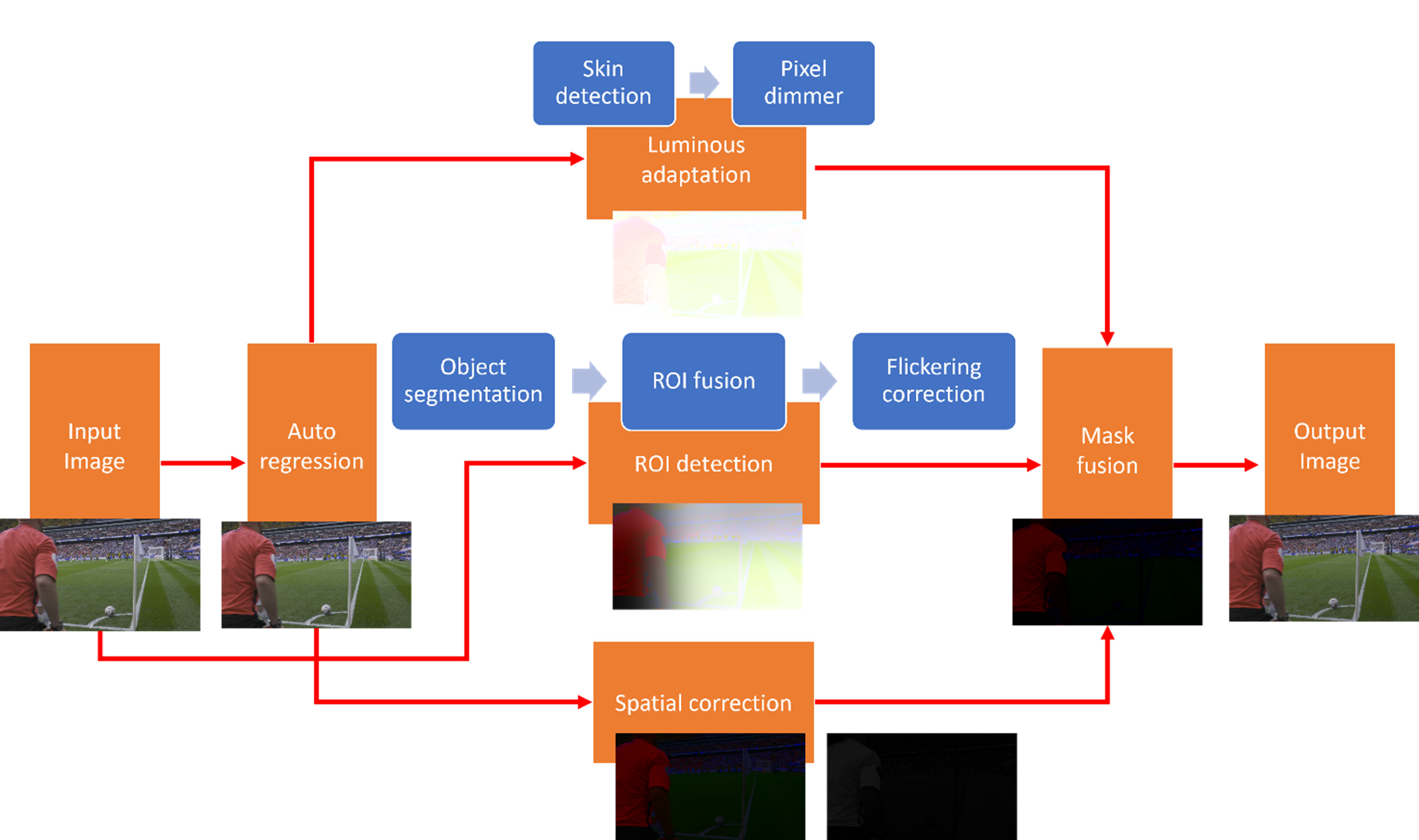
Framework of the proposed power-saving algorithms
Show energy consumption and picture luma values have a monotonic relationship, which suggests as one variable goes up or down, the opposite variable goes in the identical path. Subsequently, the above derived orderly parts are used to compute the deduction in luma values corresponding to 1 JND (i.e., the primary visible masks). In essence, they characterize the utmost energy financial savings attainable within the HDR shows for the smallest perceptible high quality distinction. Throughout this course of, we guarantee that human pores and skin tones usually are not affected, as the attention could be very delicate to pores and skin tone (i.e., pixels that correspond to human pores and skin tones usually are not modified).
A region-of-interest-based masks can be utilized, to maintain the objects inside photos minimally impacted and consequently ship many of the energy financial savings from background areas inside photos. A pre-trained mannequin is deployed for this activity.
Lastly, a spatial correction masks is employed to protect the sides of the objects, because the human eye can be delicate to variations alongside object boundaries. A sequence of gradient, gaussian and field filters are used right here to detect the sides and subsequently compute spatial correction masks.
Fifteen video sequences in three classes had been examined to guage the efficiency of the proposed strategies: sports activities, drama and nature. All had been in UHD Hybrid-Log Gamma (HLG) HDR. Three HDR TV units had been used throughout the experiments (LG-C1 OLED TV, LG-C2 OLED TV and Sony Bravia 65” ZD9 LCD TV). For the LG units, “Filmmaker” and “Customary” modes had been used, whereas for the Sony TV, “Cinema Residence” and “Customary” modes had been used.
The experimental findings affirm that energy consumption in show units is very depending on the kind of content material they show (e.g., brilliant movies eat extra energy). Moreover, the “Customary” mode in OLED TVs with further processing of video photos is linked to ~30% greater energy consumption than the equal “Filmmaker” mode. Importantly, by using the proposed energy saving algorithms, the facility consumption might be lowered as much as 18% in sure eventualities. Additional work will probably be performed on embedding chrominance info and conducting formal subjective research.
Jayasingam Adhuran additionally contributed to the work described right here.
This text first appeared in issue 59 of EBU tech-i magazine.





